Neural networks have the unique ability to derive meaning from complex and imprecise data. Neural networks can easily extract trends and patterns that are way too complicated for humans or other computer techniques to extract. Neural networks that are thoroughly trained can be thought of as ‘experts’ in the areas of information that have been given to them for analysis. Let’s take a look at six such neural networks:
1. Feedforward neural network
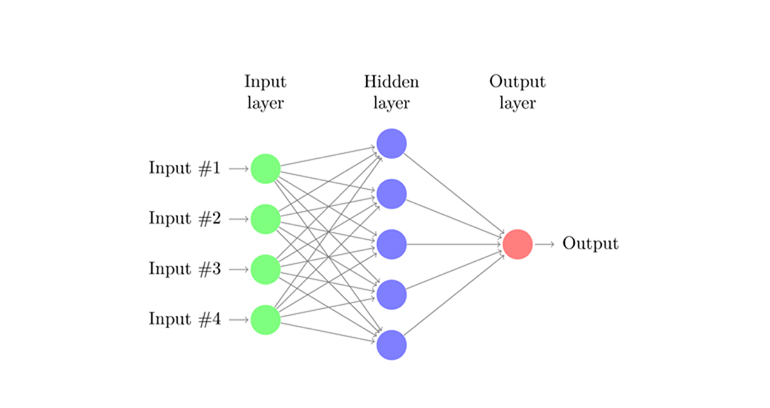
The simplest of all neural networks, the feedforward neural network, moves information in one direction only. Data moves from the input nodes to the output nodes, passing through hidden nodes (if any). The feedforward neural network has no cycles or loops in its network.
2. Radial Basis Function neural network
The RBF neural network is the first choice when interpolating in a multidimensional space. The RBF neural network is a highly intuitive neural network. Each neuron in the RBF neural network stores an example from the training set as a “prototype”. Linearity involved in the functioning of this neural network offers RBF the advantage of not suffering from local minima.
3. Kohonen self-organizing neural network
Invented by Teuvo Kohonen, the self-organizing neural network is ideal for the visualization of low-dimensional views of high-dimensional data. The self-organizing neural network is different from other neural networks and applies competitive learning to a set of input data, as opposed to error-correction learning applied by other neural networks. The Kohonen self-organizing neural network is known for performing functions on unlabeled data to describe hidden structures in it.
4. Recurrent neural network
The recurrent neural network, unlike the feedforward neural network, is a neural network that allows for a bi-directional flow of data. The network between the connected units forms a directed cycle. Such a network allows for dynamic temporal behavior to be exhibited. The recurrent neural network is capable of using its internal memory to process arbitrary sequence of inputs. This neural network is a popular choice for tasks such as handwriting and speech recognition.
5. Modular neural networks
This interesting neural network comprises of a series of independent neural networks that are moderated by an intermediary. Each of these independent neural networks works with separate inputs, accomplishing subtasks that make up the task the network as whole hopes to perform. The intermediary accepts the inputs of each of these individual neural networks, processes them, and creates the final output for the modular neural network. The independent neural networks do not interact with each other.
6. Physical neural network
This neural network aims to emphasize the reliance on physical hardware as opposed to software alone when simulating a neural network. An electrically adjustable resistance material is used for emulating the function of a neural synapse. While the physical hardware emulates the neurons, the software emulates the neural network.
Neural networks complement conventional algorithmic computers. They are versatile and can be trained to perform appropriate functions without the need for any instructions.