Blockchain technology is defined as a decentralized, distributed ledger that records the provenance of digital assets. Since its inception, blockchain is poised to be the next big technology to transform industries such as healthcare, manufacturing, logistics, and many more. Depending upon the operating model, businesses and enterprises need to choose the blockchain platform accordingly. Blockchain can be public and open, public and closed, private and open, and private and closed. When one talks about a public blockchain, the focus is usually on the public open blockchain. Similarly, when one discusses a private blockchain, the discussion is about a private closed blockchain. Let’s get to know these two blockchain types in detail.
Blockchain technology is defined as a decentralized, distributed ledger that records the provenance of digital assets. Since its inception, blockchain is poised to be the next big technology to transform industries such as healthcare, manufacturing, logistics, and many more. Depending upon the operating model, businesses and enterprises need to choose the blockchain platform accordingly. Blockchain can be public and open, public and closed, private and open, and private and closed. When one talks about a public blockchain, the focus is usually on the public open blockchain. Similarly, when one discusses a private blockchain, the discussion is about a private closed blockchain. Let’s get to know these two blockchain types in detail.
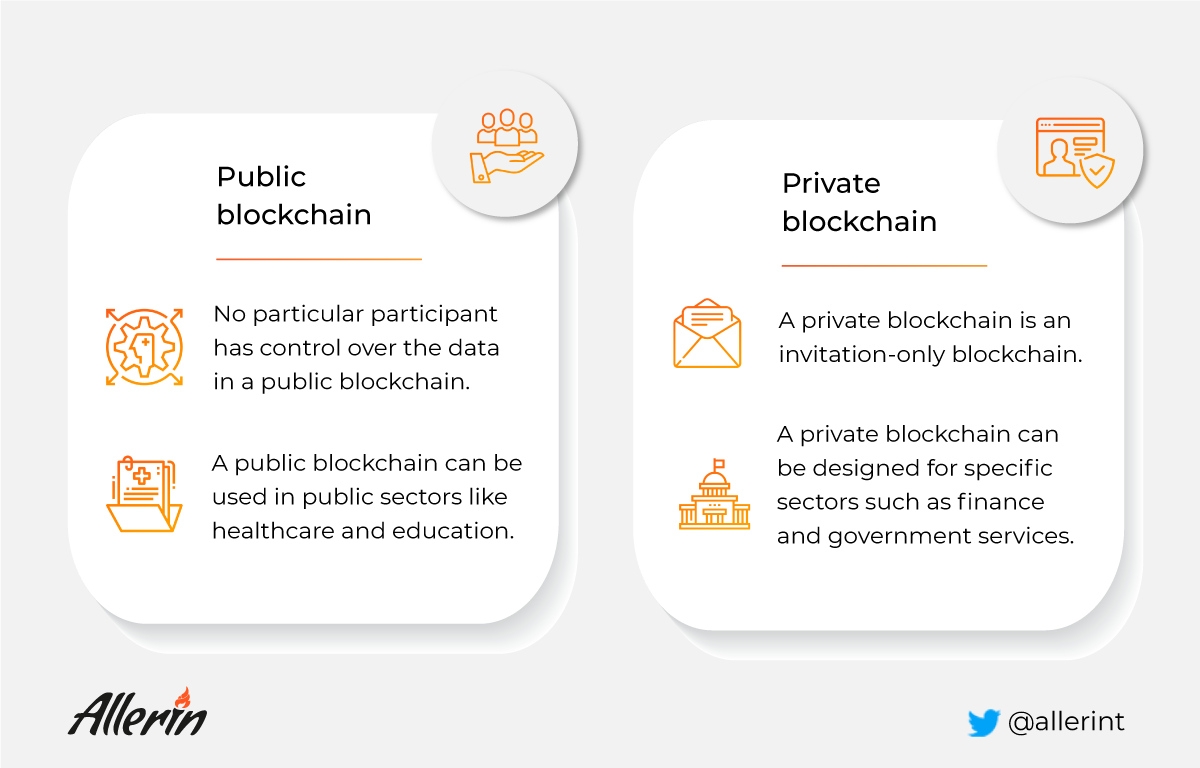
Understanding public blockchain
A public blockchain has an open network. The information is available in a public domain. Due to its permissionless nature, any party can view, read, and write data on the blockchain and the data is accessible to all. No particular participant has control over the data in a public blockchain. Public blockchains are also decentralized and immutable. It means that once an entry is made on the blockchain, it cannot be modified or deleted once the entries are validated. Some of the benefits of public blockchain are:
- Distributed ledger: All nodes in the blockchain participate in the validation of transactions.
- Open reading and writing of data: Any participating party can read, write, and view data on the blockchain.
- Immutable: Once an entry is validated, it cannot be modified or deleted.
A public blockchain sees applications in public sectors like healthcare and education. For example, healthcare institutes can use blockchain technology to have a historical record of all their operations. The data can be added by doctors and other professionals regarding the details of the patients, the cost of treatment, and other costs involved in the working of the institute. The data can be viewed by everyone on the blockchain, bringing in transparency, however, the data once added cannot be modified.
Understanding private blockchain
A private blockchain is also known as a consortium blockchain. A private blockchain is an invitation-only blockchain. The blockchain is governed by a single entity. The participating parties require permission to read, write, or audit the blockchain. The blockchain can have multiple layers of data access to keep certain pieces of data confidential. Private blockchains, therefore, ensure a higher level of security, privacy, and performance. Due to its confidential nature, private blockchains can be designed for specific sectors such as finance and government services. The transactions and data are not publicly visible and can only be accessed by the participating parties. Some of the benefits of a private blockchain are:
- Permissioned blockchain: The consortium controls the resources and access to the blockchain.
- Improved privacy: The transactions on the blockchain can only be accessed by permissioned parties.
- Increased scalability: Enterprises can add and remove nodes on demand.
Private blockchains can be adopted in the corporate sector where the details need to be shared only between certain nodes. For example, a consortium of banks can adopt a private blockchain where financial transaction details are only shared with the concerned parties.
The general consensus is that public blockchain and private blockchain are competitors. However, that is not the case. Both of these platforms serve different business scenarios. Public blockchains tend to better serve B2C players whereas private blockchain platforms are better suited to B2B scenarios. Thus, businesses should adopt a blockchain platform, i.e., public blockchain or private blockchain depending upon the functioning of the company.