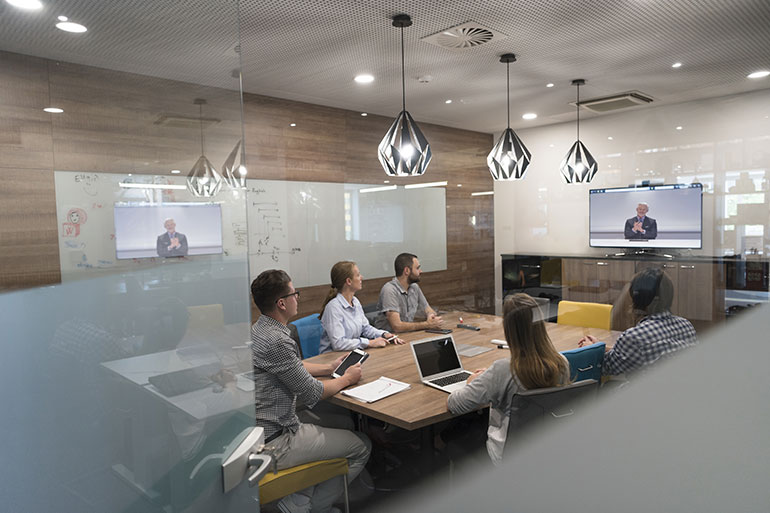
To create an efficient digital workspace, IT leaders are implementing smart workspace methods to improve productivity and information sharing. A smart workspace leverages the growing digitalization of physical objects enabled by the Internet of Things (IoT) to deliver new ways of working, sharing information and collaborating. Any location where people work can be a smart workspace. However, to do so requires IT leaders to create a unified planning framework.
There are 4 broad ways to develop a smart workspace.
Create Scenarios
IT and HR leaders must brainstorm and envision scenarios depicting the future state of a smart workspace. They must illustrate in detail, how these scenarios and digital workspaces will evolve in the future. Take an example of Peter who is a newly hired project manager in his company. As Peter walks toward the main gate of his office building, the smart workspace detects his security badge and after an authentication check, sends a recommendation to his mobile device about the best places in the building to sit. This seating suggestion is made after the smart workspace analyzes John’s work activities and schedule with his old team.
To transform such scenarios into reality, IT leaders must facilitate an open-ended brainstorming discussion with HR leaders to imagine how they can transform their workspace within three to four years.
Recognize Gaps
IT leaders should first determine strategies to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of workspaces and then decide the functional requirements and outcomes of the activities for those employees who are involved. For example,
- If the need is to reduce travel and promote virtual meetings, then a web-conferencing service could be made available.
- If the need is to improve employee access to FAQs and processing policies, in order to handle complex transactions in a better way, then a knowledge base might be integrated into the business applications to help workers quickly access relevant information.
Once you have determined the methods or ways to fulfill the functional requirements, you must identify the gaps in those requirements. For example,
- When describing the need to reduce travel through virtual meetings, a simple solution that comes across is installing a web-conferencing tool. What might not be captured is that employees can use other devices than a laptop to store their meeting-related content (such as a phone or tablet). They might require some additional tools that will allow them to collaborate and connect these devices with the web conferencing tool.
- When describing the need to improve access to job-related content while processing certain transactions, performance support solutions often assume that an employee gains access to that information through the application on a laptop. What might not be captured is that employees dealing with customers directly may not have access to a laptop, but a mobile device or a tablet instead.
Thus, IT leaders must discuss with business analysts how workspaces can be improved through better optimization of physical space and tools. Also, they must identify the areas where the existing use of productivity tools and other applications are hampered by the design of the physical space or by the absence of certain facilities such as electronic whiteboards, reservation systems, etc.
There’s more! Stay tuned for part 2 of our series on how to develop a smart workspace to gain employee engagement in our next post.