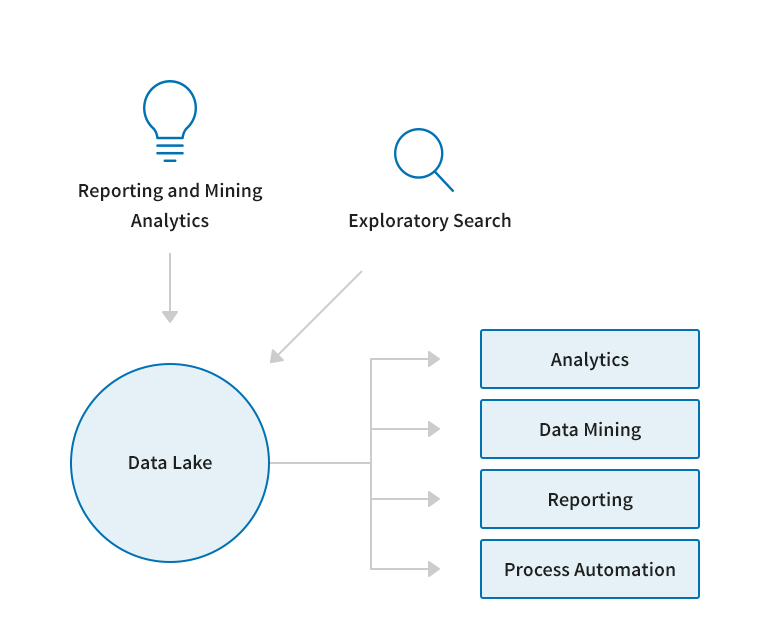
A proper framework is required to implement these iterations. Several data lake projects fail because they lack operational data flow, self-disciplined users, and appropriate data lake governance. In this blog post, we explore some measures to develop a successful data lake by learning to create a physical and logical separation of governance patterns and analytics consumption.
Data Lake Governance Measures
- For governing data in the lake, a consumer will require flexible processes to explore and search the ingested datasets in real time. By implementing metadata tagging, consumers can recognize, classify and make sense of the ingested raw data in the lake. Once the data is tagged, you can start finding datasets by inputting keywords. These keywords must refer to metadata tags. Tagging plays a significant role in managing and governing unstructured data. It captures document semantics through tags and makes the document searchable.
- Data lakes must also have the means for data custodians to monitor and assess the level of quality of data along with the ability to clean it up. Rules must be created and applied to the selected datasets that are being used currently by the business users.
- For effective governance, data analytics leaders must port newly developed analytical models and make use of integrated data. Along with this, they must execute these analytical models in an optimized environment.
- An efficiently governed data lake must provide trust and traceability of data. Data analyst leaders must implement such tools that can enable lineage metadata to automatically capture and track the original data source of data as it gets ingested in the lake. Traceability is an important aspect of data governance because, without it, lineage tools can become useless. This is because lineage tools monitor huge quantities of data, but its results cannot be trusted as the origin remains uncertain.
- Enforcing security is another important aspect of data lake governance. Any access to data must be recorded and stored for satisfying compliance audits. Data governance enables the data custodian to balance and control their datasets. Some custodians may implement strict policies and control mechanisms. This makes it easier for them to assess data and for replicating same mechanisms when data lake is implemented.
The key to determining the best level of data lake governance is to apply an efficiently executed approach. Today, implementing data lake governance policies has become a top priority for several organizations. Data lake governance depends on how organizations can create and manage metadata at the different levels.